Quiz Challenge – 30yo with Reduced Vision and Night Vision Issues
Case Study: 30yo Lady with Reduced Vision and Night Vision Issues
Dr Janice Thean
30 year old female presented with a long history of mildly reduced vision and some problems with night vision. These symptoms has been present since childhood and has not worsened over time. On examination, bilateral VAs were 6/9 with a myopic correction of -2.5 in both eyes. There were no significant past history, nor was there any family history of visual problems. OCT of her macula was normal, as were routine 24-2 visual fields. Ocular examination revealed no signs of uveitis.
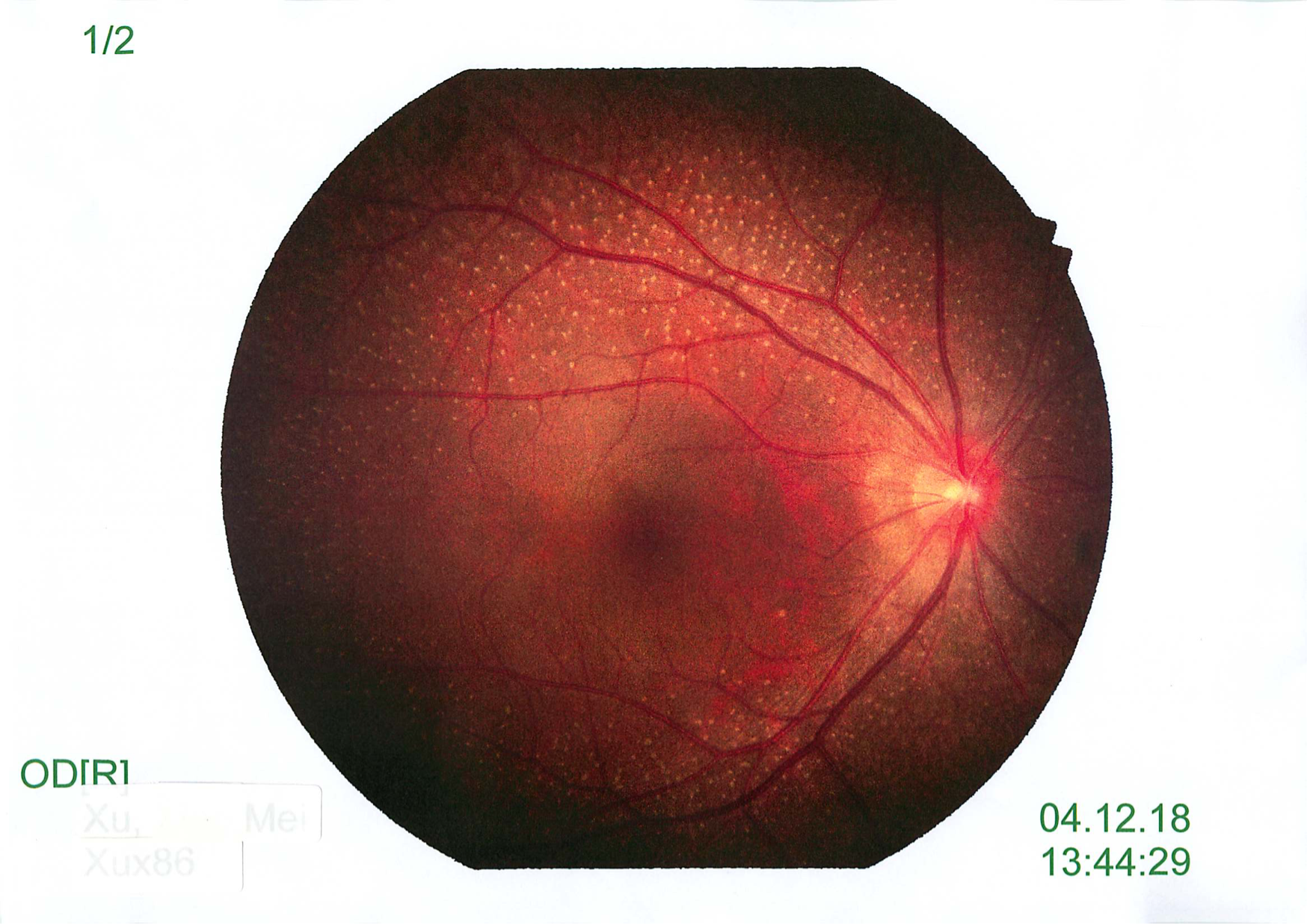
Fundus examination showed in picture below:

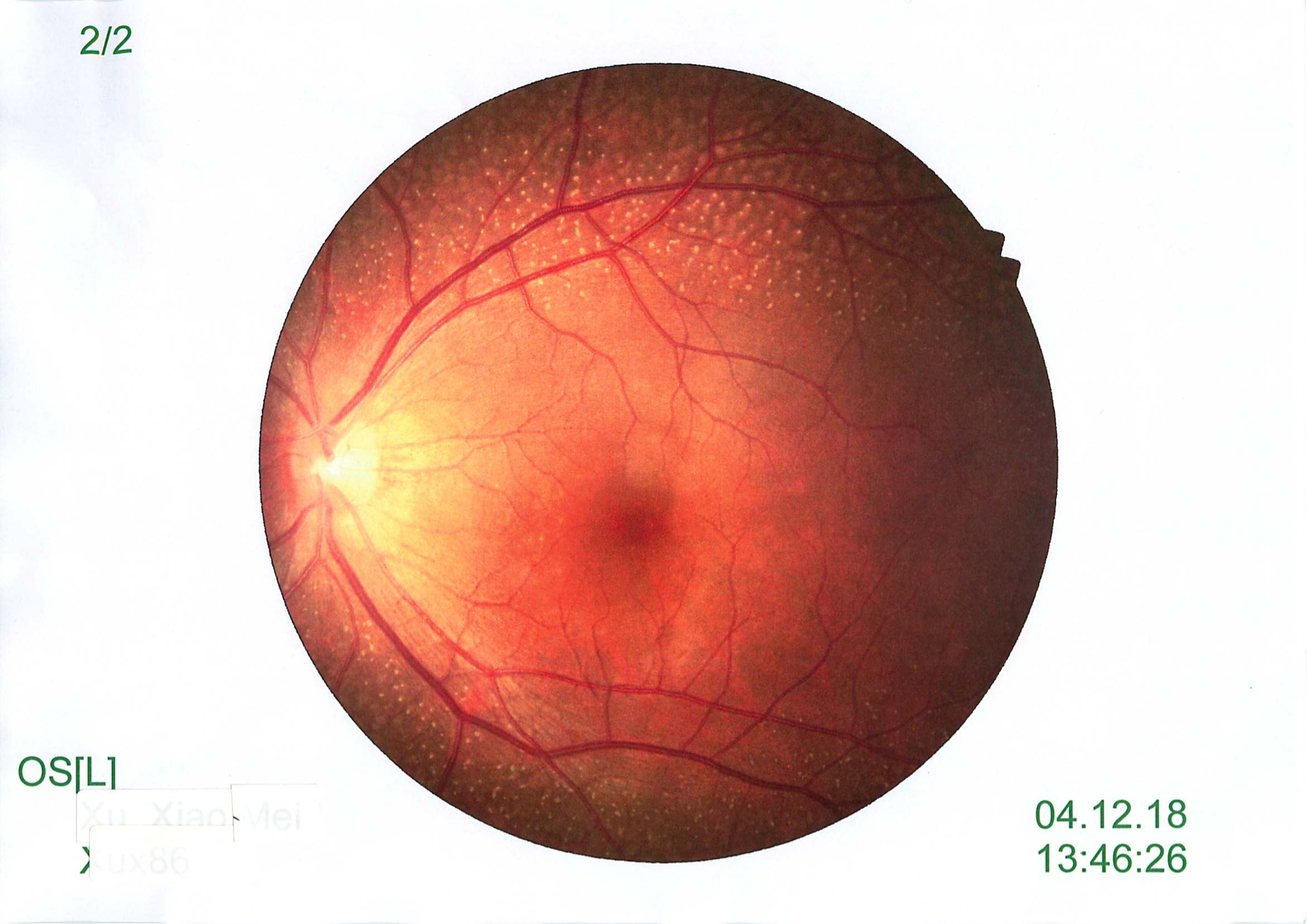
What are the differential diagnosis?
- Fundus Albipunctatus
- Retinitis Puctata Albescens
- Familial Dominant Drusen
- Fundus Flavimaculatus (Stargardts)
Click for answer.
Fundus albipunctatus (FA) is an autosomal recessive eye disorder which is part of Congential Stationary Night Blindness (CSNB). It is characterized by night blindness and the presence of whitish-yellow flecks in the retina. Individuals with fundus albipunctatus experience night blindness from an early age. In particular, they have delayed dark adaptation, which means they have trouble adapting from bright light to dark conditions, such as when driving into a dark tunnel on a sunny day. It often takes hours for adaptation to occur. Their vision in bright light is usually normal. This condition very rarely progress over time.
This is an extremely rare disorder where the prevalence is unknown. It is caused by a mutation in the RDH5 gene. This gene is involved in recycling of 11-cis retinal which is a form of vitamin A that is needed for conversion of light to electrical signals. It encodes the enzyme that is a part of the visual cycle, the 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase. The flecks are especially abundant in the mid periphery of the retina with sparing of the macula.
Electrophysiological findings, together with the appropriate genetic analysis, appear to be crucial tools in the differential diagnosis of FA. Typical ERG findings include decreased scotopic ERG responses with normalisation after 120 min of dark adaptation.